WFJL Whiteflag Messages
| WFJL Documentation Home | WFJL Javadoc Reference | Whiteflag Specification |
Overview
This section describes how Whiteflag messages are implemented internally
by the WFJL. To use Whiteflag messages in software applications, only the
org.whiteflagprotocol.java package with the WfMessage class should be
required normally.
In addition, the WfBinaryBuffer from the org.whiteflagprotocol.java.core
may be used if working with binary encoded message, but the WfMessage class
does provide methods to obtain binary encoded messages as byte arrays or
hexadecimal strings.
Example
A simplified example for creating a new Whiteflag message of a type specified by a string with the message code:
import org.whiteflagprotocol.java.WfMessage;
import org.whiteflagprotocol.java.WfException;
public class Example {
/* Properties */
private WfMessage message;
/* Methods */
public WfMessage createMessage(String messageType) throws WfException {
message = WfMessage.type(messageType);
return message;
}
}
Class Diagram
The class diagram gives a rough overview of the package. It is not intended as a complete or accurate reference for the classes. Instead, please see the WFJL Javadoc API Reference for all details.
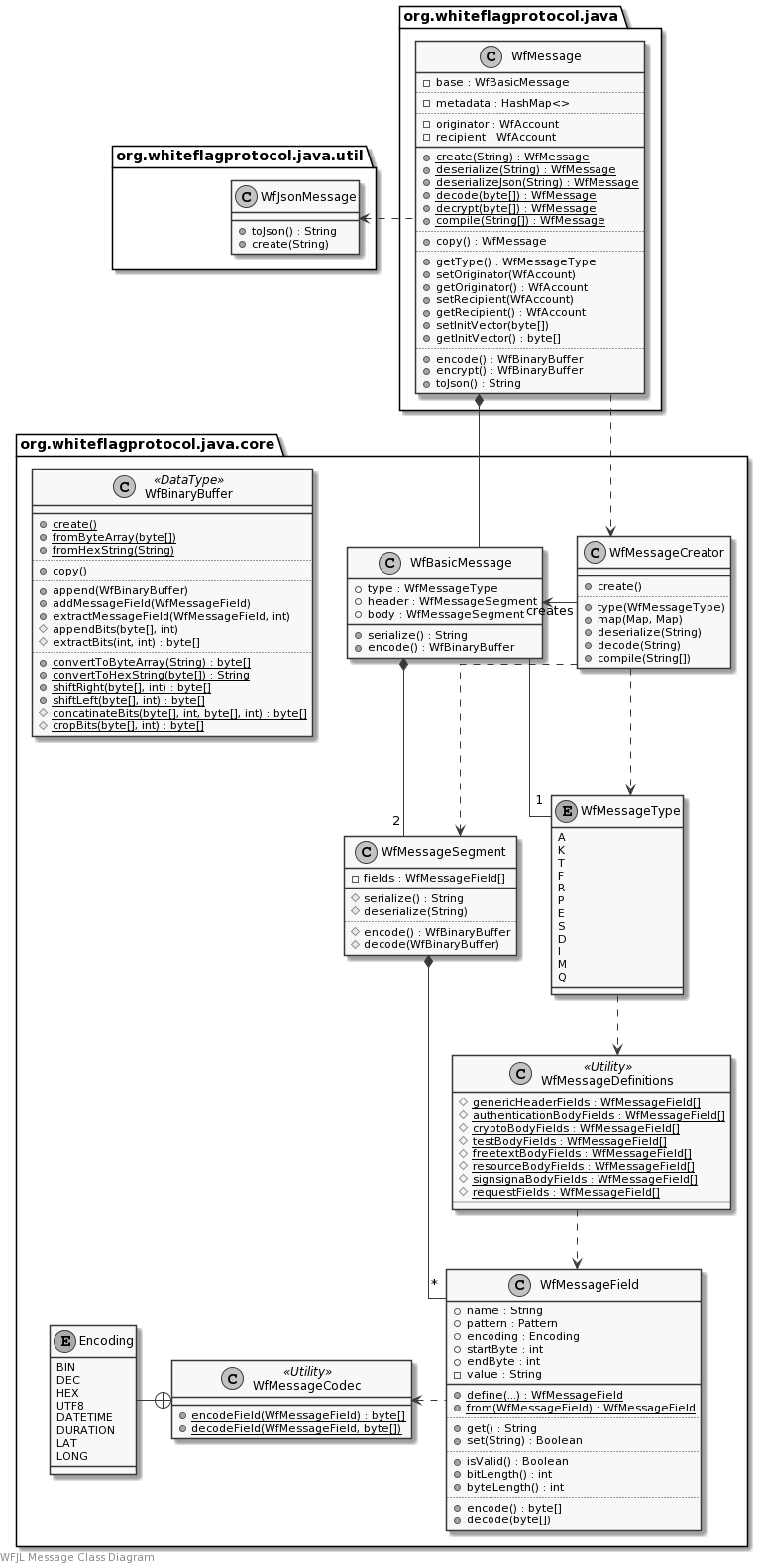
Detailed Implementation
Message Classes
The WFJL implements the Whiteflag messages defined in the Whiteflag standard
with the WfMessage class of the org.whiteflagprotocol.java package. This class
encapsulates the WfBasicMessage class from the org.whiteflagprotocol.java.core
package and adds implementation-sepcific metadata and methods that allow
for further integration in larger software applications.
Message Core, Segment and Field classes
The WfBasicMessage class only contains the elements as specified in the
Whiteflag standard, i.e. the generic message header and the message type
specific body. Both are implemented as a WfMessageSegment class, which
comprises a number of message fields implemented as WfMessageField class.
Message Creator, Type and Definition classes
To create Whiteflag messages, the core package provides the WfMessageCreator
class to instantiate WfBasicMessage objects. The WfMessageCreator class is
used by the static factory methods of the WfMessage class, which are the
external interface to other software to create Whiteflag messages.
The WfMessageType class contains all message types i.a.w. the Whiteflag
specification, and is used by the WfMessageCreator class to create the
messages. The WfMessageDefintions is a utility class with all field
definitions.
Usage
Message Creation and Alteration
The WfMessage class represents a Whiteflag message. The class cannot be
instantiated directly. Instead, one of its static factory methods must be used
to create a message. The available static factory methods to do this are:
WfMessage.type(String messageCode): creates a new Whiteflag message of the type specified by the message code with empty field valuesWfMessage.copy(WfMessage): copies an existing Whiteflag message, without the metadataWfMessage.clone(WfMessage): clones an existing Whiteflag message, including the metadataWfMessage.deserialize(String): deserializes a string with a serialized messageWfMessage.deserializeJson(String): deserializes a string with a JSON representation of a messageWfMessage.decode(String): decodes a string with the hexadecimal representation of an unencrypted encoded messageWfMessage.compile(String[]): compiles a Whiteflag message from an array with a complete and ordered set of field values
Each of these methods returns a new WfMessage object.
Message Encryption and Decryption
Message encryption and decrytion requires additional information about the
originator and recipient of the message. The encryption method is determined
by the EncryptionIndicator field in the message itself.
For encryption, the orginator and recipient information is provided by passing
account information from objects implementing the WfAccount interface through
the following methods:
WfMessage.setOriginator(WfAccount originator): sets the originator of the messageWfMessage.setRecipient(WfAccount recipient): sets the recipient of the messageWfMessage.encode()orWfMessage.encrypt(): are identical and return the binary encoded message (encrypted if theEncryptionIndicatorfield is set)WfMessage.encode().toByteArray(): returns the binary encoded/encrypted message as a byte arrayWfMessage.getInitVector(): returns the non-secret initialisation vector that is randomly created upon encryption
The non-secret initialisation vector is randomly created upon encryption, is
required for decryption. It is to be sent over the blockchain K0A Whiteflag
message. For decryption, all the information must be passed directly to the
static factory method:
WfMessage.decrypt(byte[] encryptedMsg, WfAccount originator, WfAccount recipient, byte[] initVector)
Accessing Message Fields
Message fields can be accessed through the getters and setter methods of the
WfMessage class and the fieldname:
WfMessage.set(String fieldname, String value): sets the value of the specified message fieldWfMessage.get(String fieldname): returns the value of the specified message field
To ensure data integrity, a field value cannot change once set. The set
methods returns true if the field value is set. If the return value is
false, then the field value could not be set, either because the provided
value is invalid, or the field had already been set.
See below for a number of methods to check message and field validity. Trying
to serialize or encode an invalid message will result in a WfException
of type WF_FORMAT_ERROR to be thrown.
Field Data and Validators
To support of message creation by application software, the following methods are available:
WfMessage.isValid(): returns a Boolean to indicate if the message is valid, i.e. if all message fields contain valid dataWfMessage.isValid(String fieldname): returns a Boolean to indicate if specified field contains valid dataWfMessage.isValid(String fieldname, String data): returns a Boolean to indicate if specified data would be valid for the specified fieldWfMessage.getNoFields(): returns an interger with the number of fieldsWfMessage.getFieldNames(): returns a Set with all field names
Accessing Message Msetadata
The Whiteflag message object also holds the metadata associated with the message. The metatdata may be accessed with the following methods:
WfMessage.addMetadata(String key, String value): sets the value if the key does not yet exist, otherwise it returns the existing valueWfMessage.getMetadata(String key): returns a String with the value of the provided keyWfMessage.getMetadataKeys(): returns a Set of Strings with all existing metadata keys
As described, a metadata field cannot be changed once added.